Monod´s sign in a rare case of aspergilloma
Souvik Sarkar, Babaji Ghewade
Corresponding author: Souvik Sarkar, Department of Respiratory Medicine, Datta Meghe Institute of Higher Education and Research, Wardha, Maharashtra, India 
Received: 28 Jul 2023 - Accepted: 04 Aug 2023 - Published: 22 Aug 2023
Domain: Pulmonology
Keywords: Pulmonary aspergilloma, monod´s sign, aspergillus fumigatus
©Souvik Sarkar et al. Pan African Medical Journal (ISSN: 1937-8688). This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution International 4.0 License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Cite this article: Souvik Sarkar et al. Monod´s sign in a rare case of aspergilloma. Pan African Medical Journal. 2023;45:176. [doi: 10.11604/pamj.2023.45.176.41234]
Available online at: https://www.panafrican-med-journal.com//content/article/45/176/full
Monod´s sign in a rare case of aspergilloma
&Corresponding author
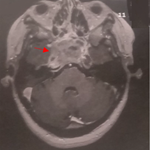
A fifty-year-old male came to the casualty with fever, chills, blood in cough, breathlessness, and right-sided chest pain for 2 months. He had a few episodes of hemoptysis approximately 5-10 ml per episode, of bright red colour. The patient was a chronic alcoholic and also had a history of tuberculosis 11 years back for which he took treatment of 6 months. On examination, he was thin built, febrile, had a pulse rate of 116 beats per minute, a blood pressure of 100/60 mmHg. On respiratory system examination a bronchial breath sound was heard in the right mammary region. A chest X-ray was done of the patient which showed fibro-bronchiectatic changes in the right upper zone. The patient also underwent high resolution computed tomography of the lungs which showed a round enhancing lesion with a surrounding air shadow seen in the superior basal segment of the right lower lobe measuring 2.5 cm x 1.6 cm in size which also changed in orientation with a change in position of the patient; Monod´s sign. Typical Monod´s sign along with air crescent sign. The patient´s serum IgE antibody for Aspergillus fumigatus was positive, and thus a diagnosis of fungal ball or aspergilloma was confirmed. The patient was started on oral Itraconazole, oral tranexamic acid which controlled the hemoptysis in a week's duration and was then referred to a thoracic surgeon for pneumonectomy.
Search
This article authors
On Pubmed
On Google Scholar
Citation [Download]
Navigate this article
Similar articles in
Key words
Tables and figures
 Figure 1: an axial section of computed tomography of lung showing a round enhancing lesion with a surrounding air shadow seen in the superior basal segment of the right lower lobe measuring 2.5 cm x 1.6 cm in size which also changed in orientation with a change in position of the patient; Monodés sign
Figure 1: an axial section of computed tomography of lung showing a round enhancing lesion with a surrounding air shadow seen in the superior basal segment of the right lower lobe measuring 2.5 cm x 1.6 cm in size which also changed in orientation with a change in position of the patient; Monodés sign