About an observation of cerebral abscess encysted
Noukhoum Koné, Sambou Soumaré
Corresponding author: Noukhoum Koné, Service de Neurochirurgie, Centre Hospitalier de Kiffa, Mauritanie 
Received: 12 Apr 2017 - Accepted: 04 Oct 2017 - Published: 21 Nov 2017
Domain: Infectious disease,Neurology (general),Neurosurgery
Keywords: Cerebral abscess, cyst, MRI
©Noukhoum Koné et al. Pan African Medical Journal (ISSN: 1937-8688). This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution International 4.0 License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Cite this article: Noukhoum Koné et al. About an observation of cerebral abscess encysted. Pan African Medical Journal. 2017;28:251. [doi: 10.11604/pamj.2017.28.251.12480]
Available online at: https://www.panafrican-med-journal.com//content/article/28/251/full
About an observation of cerebral abscess encysted
Noukhoum Koné1,&, Sambou Soumaré2
1Service de Neurochirurgie, Centre Hospitalier de Kiffa, Mauritanie, 2Centre de Radiologie, d’imagerie médicale, Centre Hospitalier de Saint Brieuc, France
&Corresponding author
Noukhoum Koné, Service de Neurochirurgie, Centre Hospitalier de Kiffa,
Mauritanie
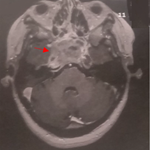
The cerebral abscess represents 2% of the intracranial lesions of the adult, 17% of the child. 35% of abscesses develop before the age of 15 years. It evolves in several phases (pre-suppurative encephalitis, purulent collection without shell, abscess collected with fine capsule, abscess collected with thick shell). We report the case of a 14-year-old girl with no specific pathological history except a neglected oral infection episode; has been present for 4 weeks with headache, vomiting, tonic-clonic convulsive seizures in a febrile context. On examination there is a proportional right hemiparesis with a motor force rated at 3/5 without facial participation, a fever at 39.5°c. The biological examination revealed a leucocytosis (17 000/mm3) predominantly neutrophilic (81%). The brain CT Scan with injection of iodinated contrast medium in axial (A) and coronal (B) sections revealed an isodense occupying process, with a left parietal seat, with annular rehabitation and partitioned, measuring 23.8mm x 20mm and presenting an edema in the satellite. Brain MRI was found 3 weeks later in sequences, T1 (C), T2 Flair (D, E), T1 gado in axial section a volumetric increase of the occupying process with a significant deviation from the line of the median structures. A craniotomy with evacuation of the abscess (F, H) and excision of the cyst wall (G) was performed. The bacteriological examination of the pus was negative. Anatomopathological examination of the cyst wall revealed non-specific inflammatory necrotic tissue. An intravenous antibiotherapy was established in post-operative stages, the clinical course proved to be significantly favorable.
Figure 1: brain CT Scan with injection of iodinated contrast medium in axial (A) and coronal (B) sections revealed an isodense occupying process, with a left parietal seat, with annular rehabitation and partitioned , measuring 23.8mm x 20mm and presenting an edema in the satellite. The brain MRI at 3 weeks later in sequences, T1 (C), T2 Flair (D, E) in axial section, volumetric increase of the occupant process with a significant deviation from the line of the median structures
Search
This article authors
On Pubmed
On Google Scholar
Citation [Download]
Navigate this article
Similar articles in
Key words
Tables and figures
 Figure 1: brain CT Scan with injection of iodinated contrast medium in axial (A) and coronal (B) sections revealed an isodense occupying process, with a left parietal seat, with annular rehabitation and partitioned , measuring 23.8mm x 20mm and presenting an edema in the satellite. The brain MRI at 3 weeks later in sequences, T1 (C), T2 Flair (D, E) in axial section, volumetric increase of the occupant process with a significant deviation from the line of the median structures
Figure 1: brain CT Scan with injection of iodinated contrast medium in axial (A) and coronal (B) sections revealed an isodense occupying process, with a left parietal seat, with annular rehabitation and partitioned , measuring 23.8mm x 20mm and presenting an edema in the satellite. The brain MRI at 3 weeks later in sequences, T1 (C), T2 Flair (D, E) in axial section, volumetric increase of the occupant process with a significant deviation from the line of the median structures