Parry-romberg syndrome: about a case
Hanane Oummad, Lalla Ouafae Cherkaoui
Corresponding author: Hanane Oummad, University of Mohamed V Souissi, Hôpital des Spécialités, Ophtalmology A Department, Morocco 
Received: 21 Feb 2017 - Accepted: 03 Jun 2017 - Published: 05 Jun 2017
Domain: Pediatric neurology,Pediatric ophthalmology,Pediatrics (general)
Keywords: Parry-romberg syndrome, hemifacial atrophy, scleroderma, hyalitis
©Hanane Oummad et al. Pan African Medical Journal (ISSN: 1937-8688). This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution International 4.0 License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Cite this article: Hanane Oummad et al. Parry-romberg syndrome: about a case. Pan African Medical Journal. 2017;27:86. [doi: 10.11604/pamj.2017.27.86.12063]
Available online at: https://www.panafrican-med-journal.com//content/article/27/86/full
Parry-romberg syndrome: about a case
Hanane Oummad1,&, Lalla Ouafae Cherkaoui2
1University of Mohamed V Souissi, Hôpital des Spécialités, Ophtalmology A Department, Morocco, 2University of Mohamed V Souissi, Hôpital des Spécialités, Ophtalmology A Department, Morocco
&Corresponding author
Hanane Oummad, University of Mohamed V Souissi, Hôpital des Spécialités, Ophtalmology A Department, Morocco
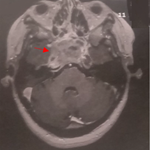
A six-year-old girl presented with skin lesions on the left cheek at 5 years of age. On examination diffuse sclerosis on the left cheek was noted, hypoplasia of left half of the face and deviation of mouth and lips to left side were noted. Investigations show normal blood counts and rheumatoid factor and antinuclear antibody were negative. CT scan of brain was normal. Fundus examination revealed a grade 2 hyalitis. Parry-romberg syndrome (PRS), also known as "progressive facial hemiatrophy" is a rare degenerative condition of the face. It is characterized by progressive but self-limiting unilateral wasting of facial skin, subcutaneous fat, muscle and occasionally bone. It can be associated with various ophthalmic and neurologic complications.
Figure 1: hypoplasia of left half of the face and deviation of mouth and lips to the left side