Adénocarcinome ano-réctal après traitement par Infliximab pour une maladie de Crohn fistulisante
Jihane Smaali, Youssef Sekkach
Corresponding author: Youssef Sekkach, Département de Médecine Interne, Hôpital Militaire d'Instruction Mohammed V, Université Med V, Souissi, Rabat, Maroc 
Received: 02 Jul 2016 - Accepted: 07 Mar 2017 - Published: 24 Mar 2017
Domain: Clinical medicine
Keywords: Maladie de Crohn, infliximab, adénocarcinome ano-réctal
©Jihane Smaali et al. Pan African Medical Journal (ISSN: 1937-8688). This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution International 4.0 License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Cite this article: Jihane Smaali et al. Adénocarcinome ano-réctal après traitement par Infliximab pour une maladie de Crohn fistulisante. Pan African Medical Journal. 2017;26:172. [doi: 10.11604/pamj.2017.26.172.10218]
Available online at: https://www.panafrican-med-journal.com//content/article/26/172/full
Original article 
Adénocarcinome ano-réctal après traitement par Infliximab pour une maladie de Crohn fistulisante
Adénocarcinome ano-réctal après traitement par Infliximab pour une maladie de Crohn fistulisante
Anorectal adenocarcinoma after Infliximab treatment for fistulizing Crohn's disease
Jihane Smaali1,&, Youssef Sekkach1
1Département de Médecine Interne, Hôpital Militaire d'Instruction Mohammed V, Université Med V, Souissi, Rabat, Maroc
&Auteur correspondant
Youssef Sekkach, Département de Médecine Interne, Hôpital Militaire d'Instruction Mohammed V, Université Med V, Souissi, Rabat, Maroc
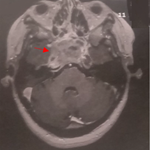
We here report the case of a 35-year patient treated for anoperineal Crohn's disease with corticosteroids and then 6-mercaptopurine and azathioprine inducing prolonged remission. Patient's evolution was marked by fast deterioration of general health status. Morphological examination were in favor of severe outbreak of disease. The diagnosis of fistulizing anoperineal Crohn's disease was made (A). The patient was treated with broad-spectrum antibiotics, parenteral feeding, digestive system at rest and defunctioning colostomy allowing clinical improvement. Then he was treated with anti-TNF-alpha Infliximab at a dosage of 5mg/kg (S0, S2, S4 and S8). Patient's evolution was complicated by the gradual onset of a tumor-like anal lesion (B) progressively increasing its volume associated with fast deterioration of general health status. New abdominal MRI allowed to detect anorectal tumoral process, immunohistochimically in favor of infiltrating ano-rectal adenocarcinoma. 4.3% of cases with anorectal adenocarcinoma associated with fistulizing Crohn's disease have been reported. This study aimed to attentively analyse possible malignant transformation of fistulizing Crohn's disease in any patient treated with infliximab and to highlight the role of histological assessment of any anal or perineal lesion before treatment with anti-TNF therapy. Diagnosis is difficult because due to inflammatory status and/or concomitant stenosis; imaging tests, including CT scan and MRI appear to have a low sensitivity in detecting cancer.
Key words: Crohn disease, infliximab, anorectal adenocarcinoma
Patient de 35 ans, suivi pour une maladie de Crohn anopérinéale traitée par corticoides puis, 6-mercaptopurine et azathioprine, avec une rémission prolongée. Durant l'évolution, le patient présenta une altération rapide de l'état général. Les investigations morphologiques étaient en faveur d'une poussée grave dans le cadre de sa maladie. Le diagnostic d'une maladie de Crohn ano-périnéale dans sa forme fistulisante était posé (A), et le patient avait bénéficiée d'une antibiothérapie à large spectre, une alimentation parentérale, une mise au repos du tube digestif et une colostomie de décharge ayant permis une amélioration clinique, puis la mise sous anti-TNF alpha type Infliximab à la dose de 5mg/kg (S0, S2, S4 et S8). L'évolution s'est compliquée de l'apparition progressive d'une lésion anale d'allure tumorale (B) augmentant progressivement de volume avec altération rapide de l'état général. Une nouvelle imagerie abdominale (IRM) permettait d'individualiser un processus ano-réctal d'allure tumorale, immunohistochimiquement en faveur d'un adénocarcinome ano-rectal infiltrant. 4,3% de cas d'adénocarcinome ano-rectaux sur maladie de crohn fitulisante ont été rapportés. A la lumière de cette illustration, nous accordons une attention très particulière sur la possible transformation maligne chez tout patient traité par Infliximab pour une maladie de Crohn fistulisante, et nous insistons sur une évaluation histologique de toute lésion anale ou périnéale avant traitement par anti-TNF. Le diagnostic reste difficile en raison des phénomènes inflammatoires et / ou des sténoses concomitantes; Les moyens d'imagerie, y compris les examens TDM et l'IRM semblent avoir une faible sensibilité dans la détection du cancer.
Figure 1: A) maladie de Crohn fistulisante avant infliximab; B) maladie de crohn fistulisante après infliximab