Fibre à myéline: diagnostic différentiel de l’œdème papillaire
Aniss Regragui, Rajae Daoudi
Corresponding author: Aniss Regragui, Université Mohammed V Souissi, Service d’Ophtalmologie A de l’Hôpital des Spécialités, Centre Hospitalier Universitaire, Rabat, Maroc 
Received: 30 Sep 2014 - Accepted: 21 Oct 2014 - Published: 27 Sep 2016
Domain: Public Health
Keywords: Fibre à myéline, oedème papillaire, myopie
©Aniss Regragui et al. Pan African Medical Journal (ISSN: 1937-8688). This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution International 4.0 License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Cite this article: Aniss Regragui et al. Fibre à myéline: diagnostic différentiel de l’œdème papillaire. Pan African Medical Journal. 2016;25:33. [doi: 10.11604/pamj.2016.25.33.5523]
Available online at: https://www.panafrican-med-journal.com//content/article/25/33/full
Fibre à myéline: diagnostic différentiel de l’œdème papillaire
Myelinated fiber: differential diagnosis of papilledema
Aniss Regragui1, &, Rajae Daoudi1
1Université Mohammed V Souissi, Service d’Ophtalmologie A de l’Hôpital des Spécialités, Centre Hospitalier Universitaire, Rabat, Maroc
&Auteur correspondant
Aniss Regragui, Université Mohammed V Souissi, Service d’Ophtalmologie A de l’Hôpital des Spécialités, Centre Hospitalier Universitaire, Rabat, Maroc
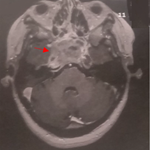
This study reports the case of a 32-year-old female patient with no particular history, treated for myopia since school age. Routine ocular examination showed visual acuity value 10/10, clear cornea, anterior chamber, good depth, with normal iris texture and color and clear lens in both eyes with intraocular pressure 16 mmHg in the right eye and 14 mmHg in the left eye. Fundus examination showed papillary excavation 3/10 in the left eye with a whitish stain poorly limited and contiguous edge blurred at the nasal side of the papilla evoking myelinated fiber, the fellow eye was unremarkable. Retinal fluorescein angiography showed no delayed filling or signs of early or late leakage eliminating papilloedema. Myelinated fibers are asymptomatic benign lesions which may be detected, often incidentally, during fundus examination and which can be associated with a refractive error such as myopia. They should be considered as differential diagnosis of papillary edema.
Key words: Fiber myelin, papilledema, myopia
La patiente présente dans ce cas est âgée de 32 ans, sans antécédents particuliers et suivie pour myopie depuis l'âge scolaire, lors d'un examen de routine; on trouve au niveau des 2 yeux une acuité visuelle a 10/10 une cornée claire, une chambre antérieure, de bonne profondeur, un iris de trame et coloration normale et un cristallin clair avec un tonus oculaire a 16 mmhg à l'oeil droit et 14 mmhg à l'oeil gauche. L'examen du fond d'oeil trouve au niveau de l'oeil gauche une papille d'excavation 3/10 avec une tache blanchâtre mal limitée à bord flou contiguë au bord nasal de la papille évoquant l'aspect de fibre a myéline, l'oeiladélphe est sans particularités. L'angiographie à la fluoresceïne rétinienne ne montre ni retard de remplissage ni des signes de fuite précoce ou tardif éliminant l'œdème papillaire. Les fibres à myéline c'est une pathologie bénigne asymptomatique de découverte fortuite lors d'un examen de fond d'oeil et qui peut être associé a un vice réfractif le plus souvent la myopie et réalisant un diagnostic différentiel devant l'aspect d'œdème papillaire.
Figure 1: tâche blanchâtre mal limitée à bord flou contiguë au bord nasal de la papille évoquant l’aspect de fibre a myéline