Agénésie de l’artère pulmonaire gauche
Hicham Naji-Amrani, Yasmina Rhofir
Corresponding author: Hicham Naji-Amrani, Service de Pneumologie, Hôpital Militaire d’Instruction Mohammed V, Rabat, Maroc 
Received: 24 Jul 2016 - Accepted: 04 Aug 2016 - Published: 21 Nov 2016
Domain: Clinical medicine
Keywords: Artère pulmonaire, agénésie, cardiopathie congénitale
©Hicham Naji-Amrani et al. Pan African Medical Journal (ISSN: 1937-8688). This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution International 4.0 License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Cite this article: Hicham Naji-Amrani et al. Agénésie de l’artère pulmonaire gauche. Pan African Medical Journal. 2016;25:181. [doi: 10.11604/pamj.2016.25.181.10388]
Available online at: https://www.panafrican-med-journal.com//content/article/25/181/full
Agénésie de l’artère pulmonaire gauche
Left pulmonary artery agenesis
Hicham Naji-Amrani1,&, Yasmina Rhofir1
1Service de Pneumologie, Hôpital Militaire d’Instruction Mohammed V, Rabat, Maroc
&Auteur correspondant
Hicham Naji-Amrani, Service de Pneumologie, Hôpital Militaire d’Instruction Mohammed V, Rabat, Maroc
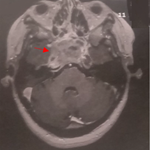
Unilateral pulmonary artery agenesis is a rare malformation accounting for 1% of congenital heart defects. It can lead to several complications. We report the case of a 16-year-old female patient with no particular past medical history, presenting with recurrent low abundance hemoptysis within a context of preservation of patient’s general condition. Clinical examination showed no abnormalities and frontal (A) and lateral (B) chest x-ray revealed small left lung-field associated with decreased vascular pattern and mediastinal shift to the left. Given this radio-clinical presentation, diagnosis of suspected left pulmonary hypoplasia, sequelae of a previous pulmonary infection and endobronchial foreign body were made. Thoracic CT scan objectifies the absence of left pulmonary artery (C) and multiple systemic collateral circulation Left pulmonary parenchyma was hypoplastic, well ventilated and without bronchial abnormality (D). The descending aorta was located on the right. The electrocardiogram showed right bundle-branch block and transthoracic ultrasound did not reveal cardiac abnormality including sign of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Spirometry showed normal respiratory function as well as laboratory tests. Hemoptysis treatment was symptomatic and the patient was kept under medical monitoring.
Key words: Pulmonary artery, agenesis, congenital cardiopathy
L’agénésie unilatérale de l’artère pulmonaire est une malformation rare concernant 1% des cardiopathies congénitales et qui peut être source de plusieurs complications. Nous rapportons le cas d’une jeune patiente âgée de 16 ans, sans antécédents pathologiques, présentant une hémoptysie de faible abondance récidivante dans un contexte de conservation de l’état général. L’examen clinique est sans anomalie et la radiographie thoracique de face (A) et de latéral (B) montre un aspect de petit champ pulmonaire gauche, une diminution de la trame vasculaire avec déviation du médiastin à gauche. Devant ce tableau radio-clinique on a évoqué une hypoplasie pulmonaire gauche, séquelles d’infection pulmonaire anciennes ou un corps étranger endobronchique. L’angioscanner thoracique objective l’absence de l’artère pulmonaire gauche (C) avec de nombreuses collatérales systémiques. Le parenchyme pulmonaire gauche est hypoplasique, bien aéré et sans anomalie bronchique (D). À noter que l’aorte descendante est située à droite. L’électrocardiogramme montre un aspect de bloc de branche droit et l’échographie trans-thoracique ne trouve pas d’anomalie cardiaque notamment pas de signe d’hypertension artérielle pulmonaire. La fonction respiratoire à la spiromètrie est normale ainsi que les examens biologiques. L’hémoptysie a été contrôlée par traitement symptomatique et la patiente est sous surveillance médicale.
Figure 1: (A, B) radiographie thoracique de face et de profil montrant un petit champ pulmonaire gauche avec déviation médiastinale gauche; C) fenêtre médiastinale de l’angioscanner thoracique objectivant l’absence de l’artère pulmonaire gauche et l’aorte descendante placée à droite; D) fenêtre parenchymateuse du scanner thoracique montrant un poumon gauche hypoplasique mais bien aéré
Search
This article authors
On Pubmed
On Google Scholar
Citation [Download]
Navigate this article
Similar articles in
Key words
Tables and figures
 Figure 1: (A, B) radiographie thoracique de face et de profil montrant un petit champ pulmonaire gauche avec déviation médiastinale gauche; C) fenêtre médiastinale de l´angioscanner thoracique objectivant l´absence de l´artère pulmonaire gauche et l´aorte descendante placée à droite; D) fenêtre parenchymateuse du scanner thoracique montrant un poumon gauche hypoplasique mais bien aéré
Figure 1: (A, B) radiographie thoracique de face et de profil montrant un petit champ pulmonaire gauche avec déviation médiastinale gauche; C) fenêtre médiastinale de l´angioscanner thoracique objectivant l´absence de l´artère pulmonaire gauche et l´aorte descendante placée à droite; D) fenêtre parenchymateuse du scanner thoracique montrant un poumon gauche hypoplasique mais bien aéré