La pyélonéphrite xanthogranulomateuse
Ali Beddouche, Ousmane Nago Dembele
Corresponding author: Ali Beddouche, Service d’Urologie A, Hôpital Ibn Sina, CHU Rabat, Maroc 
Received: 11 Apr 2016 - Accepted: 26 Apr 2016 - Published: 27 May 2016
Domain: Clinical medicine
Keywords: Pyélonéphrite, xanthogranulomateuse, parenchyme, pseudo-kystes
©Ali Beddouche et al. Pan African Medical Journal (ISSN: 1937-8688). This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution International 4.0 License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Cite this article: Ali Beddouche et al. La pyélonéphrite xanthogranulomateuse. Pan African Medical Journal. 2016;24:91. [doi: 10.11604/pamj.2016.24.91.9598]
Available online at: https://www.panafrican-med-journal.com//content/article/24/91/full
La pyélonéphrite xanthogranulomateuse
Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis
Ali Beddouche1,&, Ousmane Nago Dembele1
1Service d’Urologie A, Hôpital Ibn Sina, CHU Rabat, Maroc
&Auteur correspondant
Ali Beddouche, Service d’Urologie A, Hôpital Ibn Sina, CHU Rabat, Maroc
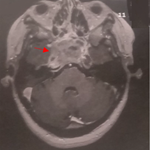
Mrs LF 46 years old, with no particular history. She presented with left lower back pain. Clinically she was febrile at 38.8°C, dipstick urinalysi (nitrites, leukocytes +). Physical examination revealed pain during palpation over the left lumbar region. Laboratory tests objectified leukocytosis 22400/mm3, C-reactive protein (CRP) levels of 124 mg/l, and urinalysis test revealed multiple-antibiotic-resistant Escherichia Coli infection in the urine. Radiologically, abdominal ultrasound highlighted a significant left pelvicalyceal dilation with finely echogenic content and reduced cortical index. The CT urography showed increased left kidney size, seat of multiple intraparenchymal fluid, pseudo-cystics, heterogeneous and compartmentalized cavities, with major parenchymal atrophy, excretory delay, and significant perirenal fat infiltration associated with lithiasis of the lumbar ureter measuring 12 mm. The scannographic image allowed us to suggest the following diagnosis: diffuse xanthogranulomateuse pyelonephritis (XGP), multicystic kidney with pyonephrosis, kidney tumor necrosis (clear cell carcinoma...). Radical nephrectomy was performed, the diagnosis of XGP was retained after histopathological examination of the surgical specimen.
Key words: Pyelonephritis, xanthogranulomatous, parenchyma, pseudocysts
Madame LF âgée de 46 ans, sans antécédents particuliers. Elle avait consulté pour des lombalgies gauches. Cliniquement elle était fébrile à 38,8°C, bandelettes urinaires (Nitrites, leucocytes +). L'examen mettait en évidence un contacte lombaire gauche douloureux. Le bilan biologique avait objectivé une hyperleucocytose à 22400/mm3, une CRP à 124 mg/l, et l'ECBU a mis en évidence une infection urinaire à Escherichia Coli multi-sensible à l'antibiogramme. Sur le plan radiologique l'échographie abdominale mettait en évidence une importante dilatation pyélocalicielle gauche à contenu finement échogène, avec réduction de l'index corticale. L'uroscanner retrouvait un rein gauche augmenté de taille, siège de multiples cavités liquidiennes intra-parenchymateuses, pseudo-kystiques, hétérogènes et cloisonnées, avec atrophie parenchymateuse majeure, retard excrétoire, et importante infiltration de la graisse péri-rénale, sur une lithiase de l'uretère lombaire de 12mm. L'aspect scannographique nous a permis d'évoquer les diagnostics suivant: une pyélonéphrite xanthogranulomateuse (PXG) diffuse, une pyonéphrose sur rein multi-kystique, une tumeur rénale nécrosée (carcinome a cellules claires...). Une néphrectomie totale élargie a été réalisée, le diagnostic de PXG fut retenu après examen anatomopathologique de la pièce opératoire.
Figure 1: A) TDM: formations pseudo-kystiques rénales gauches; B) pièce de néphrectomie