Image en popcorn cérébrale
Rachid Ammor, Assou Ajja
Corresponding author: Rachid Ammor, Hôpital Militaire My Ismael, Meknès, Maroc 
Received: 07 Dec 2015 - Accepted: 31 Dec 2015 - Published: 08 Jan 2016
Domain: Clinical medicine
Keywords: Crises convulsives généralisées, IRM cérébrale, image en pop corn, traitement antiépileptique
©Rachid Ammor et al. Pan African Medical Journal (ISSN: 1937-8688). This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution International 4.0 License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Cite this article: Rachid Ammor et al. Image en popcorn cérébrale. Pan African Medical Journal. 2016;23:3. [doi: 10.11604/pamj.2016.23.3.8583]
Available online at: https://www.panafrican-med-journal.com//content/article/23/3/full
Image en popcorn cérébrale
Brain popcorn image
Rachid Ammor1,&, Assou Ajja1
1Hôpital Militaire My Ismael, Meknès, Maroc
&Auteur correspondant
Rachid Ammor, Hôpital Militaire My Ismael, Meknès, Maroc
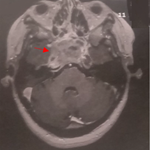
Cerebral cavernous are vascular lesions defined by the presence of deformed capillaries without interposition of nervous tissue. These are relatively rare (0.1 to 0.5% of the general population and less than 5% are symptomatic), clinical symptomatology is dominated by hemorrhage and epilepsy, and also depends on the location. Cerebral MRI is the gold standard for diagnosis, therapeutic approach and following. We report the clinical case of 27 old man, with no history, who presented two generalized convulsive seizures a week ago. Clinical examination was normal. Brain MRI has objectified a left frontal lesion with typical appearance in popcorn and combining hyper signal (recent bleeding or calcifications) and hypo signal (hemosiderin deposition bleeding = old) on T2-weighted images. The patient was put under antiepileptic treatment (valproic acid) with total seizure control.
Key words: Generalized seizures, brain MRI, image popcorn, antiepileptic treatment
Les cavernomes cérébraux sont des lésions vasculaires définies par la présence de capillaires malformés sans interposition de tissu nerveux. Ce sont des lésions relativement rares (0,1à 0,5% de la population générale dont moins de 5% sont symptomatiques), la symptomatologie clinique est dominée par l'hémorragie et l'épilepsie et dépend aussi de la localisation. L'IRM cérébrale est l'examen de référence pour le diagnostic, l'approche thérapeutique et le suivi. Nous rapportons ici l'observation clinique d'un jeune homme de 27 ans, sans antécédents, qui a présenté deux crises convulsives généralisées à une semaine d'intervalle. L'examen clinique a été normal. L'IRM cérébrale a objectivé une lésion frontale gauche avec aspect typique en pop corn ou poivre et sel associant hyper signal (saignement récent ou calcifications) et hypo signal (dépôt d'hémosidérine=saignement ancien) sur les séquences pondérées T2. Le patient a été mis sous traitement antiépileptique a base d'acide valproïque avec contrôle total des crises.
Figure 1: IRM cérébrale en coupe axiale séquence pondérée T2, montrant une lésion frontale gauche en hyper et hypo signal de 2,2/2,5cm