Thrombosis with Behçets disease should be evaluated different conditions
Ilknur Balta, Sevket Balta, Mustafa Demir, Cengiz Ozturk, Sait Demirkol
Corresponding author: Ilknur Balta, Department of Cardiology, Eskisehir Military Hospital, Eskisehir, Turkey 
Received: 08 Nov 2013 - Accepted: 06 Feb 2015 - Published: 10 Feb 2015
Domain: Clinical medicine
Keywords: Thrombosis, Behçet´s disease, massive pulmonary
©Ilknur Balta et al. Pan African Medical Journal (ISSN: 1937-8688). This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution International 4.0 License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Cite this article: Ilknur Balta et al. Thrombosis with Behçets disease should be evaluated different conditions. Pan African Medical Journal. 2015;20:117. [doi: 10.11604/pamj.2015.20.117.3571]
Available online at: https://www.panafrican-med-journal.com//content/article/20/117/full
Thrombosis with Behçets disease should be evaluated different conditions
Ilknur Balta1,&, Sevket Balta2, Mustafa Demir3, Cengiz Ozturk2, Sait Demirkol3
1Department of Dermatology, Kecioren Training and Research Hospital, Ankara, Turkey, 2Department of Cardiology, Eskisehir Military Hospital, Eskisehir, Turkey, 3Department of Cardiology, Gulhane Medical Academy, Ankara, Turkey
&Corresponding author
Ilknur Balta, Department of Cardiology, Eskisehir Military Hospital, Eskisehir,
Turkey
Dear Editor,
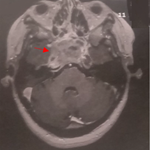
We read the article Intracardiac thrombosis in Behçets disease: a rare complication by Ghita Saghi et al with interest [1]. The authors reported a case with mobile thrombus in the right ventricle and a massive pulmonary embolism by a magnetic resonance Imaging scan (MRI), which was successfully treated conservatively.
Vascular involvement and thrombotic tendency is a potentially lifethreatening condition in patients with Behçet´s disease. Deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism are the most common manifestation but other locations may also occur. A risk factor of thrombosis was observed in many patients. Most of patients have commonly a tendency to be thrombophilias including hereditary thrombophilia, an antiphospholipids syndrome, Behçet´s disease and neoplasia. Medical therapy and surgical resection can be mentioned these thrombotic complication. Surgical treatment could be considered because the right atrial thrombus was mobile and it caused a massive pulmonary embolism.
We previously reported case of a 48-year-old male patient with Behçets disease who presented with right heart thrombus dissolved after medical management [2]. In this case, because many conditions could cause thrombotic events [3], we investigated the hypercoagulability tendeny conditions including the higher protein C, protein S, homocystine and positive antiphospholipid antibodies. We also analysed the prothrombin gene and Factor V Leiden mutation. Because differential diagnosis for thrombosis is an important for these conditions, the authors had mentioned these factors.
Furthermore, in a previous case report, the authors reported a case with diffuse thrombosis extending from vena cava superior to brachiocephalic vein accompanied by dural sinus thrombosis, which was successfully treated with oral anticoagulant and thrombolytic therapy. After warfarin therapy a significant drop in hemoglobin level occurred. The anticoagulant therapy was stopped due to suspected GIS hemorrhage and antiaggregant therapy was replaced. In this context, thrombolytic and warfarin treatment should not be withheld if necessary, because they may lead to serious complications [4]. As a conclusion, a case with with mobile thrombus in the right ventricle and a massive pulmonary embolism by a magnetic resonance Imaging scan (MRI), which was successfully treated conservatively as presented in current case report. However, thrombotic events may be associated very different conditions and warfarin treatment may cause serious complications and the pivotal roles of those factors evaluate further reports.
The authors declare no competing interest.
All authors read and agreed to the ?nal version of this manuscript.
- Saghi G, Doghmi N. Intracardiac thrombosis in Behçets disease: a rare complication. Pan Afr Med J. 2013 Jan;15:91. PubMed | Google Scholar
- Balta I, Balta S, Demirkol S, Unlu M. Right Heart Thrombus Dissolved After Medical Management in a Patient with Behçets Disease. Gulhane Med J (In press). 2013. PubMed | Google Scholar
- Balta I, Balta S, Demir M, Ozturk C, Demirkol S. Thrombotic Events in Behçets Disease. Am J Emerg Med (Article in press). 2013. PubMed | Google Scholar
- Celik G, Yildirim E, Narci H, Ozülkü M. Diffuse thrombosis secondary to Behçets disease: a case report. Am J Emerg Med (Article in press). 2013. PubMed | Google Scholar