Intracardiac thrombosis in BehÁetís disease: a rare complication
Ghita Saghi, Nawal Doghmi
Corresponding author: Ghita Saghi, Cardiologie B, CHU IBN SINA, Rabat, Maroc 
Received: 23 Mar 2013 - Accepted: 21 Jun 2013 - Published: 09 Jul 2013
Domain: Clinical medicine
Keywords: Thrombosis, Behçetís disease, pulmonary embolism
©Ghita Saghi et al. Pan African Medical Journal (ISSN: 1937-8688). This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution International 4.0 License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Cite this article: Ghita Saghi et al. Intracardiac thrombosis in BehÁetís disease: a rare complication. Pan African Medical Journal. 2013;15:91. [doi: 10.11604/pamj.2013.15.91.2635]
Available online at: https://www.panafrican-med-journal.com//content/article/15/91/full
Intracardiac thrombosis in BehÁetís disease: a rare complication
Ghita Saghi1,&, Nawal Doghmi1
1Cardiologie B, CHU IBN SINA, Rabat, Maroc
&Corresponding author
Ghita Saghi, Cardiologie B, CHU IBN SINA, Rabat, Maroc
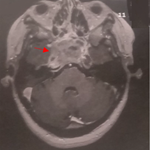
A 13 year-old boy with BD since 2007 was admitted in May 2012 for dyspnea and prolonged fever for 2 months. A physical examination did not reveal signs of heart failure. Transthoracic echocardiography showed a homogeneous mass attached to the right ventricle. We complemented with an magnetic resonance Imaging scan (MRI) that revealed a voluminous, mobile thrombus in the right ventricle and a massive pulmonary embolism. We opted for a conservative treatment: Heparin, oral anticoagulation and Methylprednisolone followed by Prednisone . The outcome was favorable under medical treatment. Cardiovascular disease in BehÁet?s disease varies from 7 to 29% of reported cases and is represented mainly by endocarditis, pericarditis and myocardial infarction. Intracardiac thrombosis (ICT) is exceptional and can since the first case described at necropsy by Buge in 1977, only about 50 cases of ICT have been reported. The association with pulmonary embolism is serious and life-threatening.
Figure 1: Cardiac magnetic resonance image, heart four chambers view showing right ventricle thrombus (arrow)